~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
21-04-2024 - Economy - Production factors [EN]-[IT]
Production factors
Note
The factor market is made up of labor and capital.
In this market, supply is the supply of labor by workers and demand is the demand for labor by employers. The price is the wage.
In the labor market, workers are free to enter and exit whenever they want, while companies can change the quantity of labor employed.
Labor market in graphs
Graphic example of the apple market
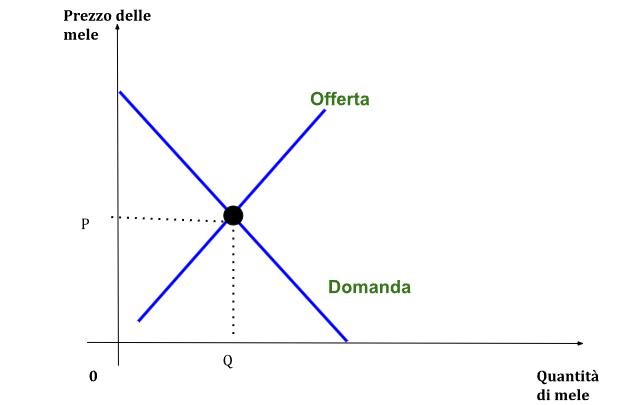
Apple Pickers Market Chart
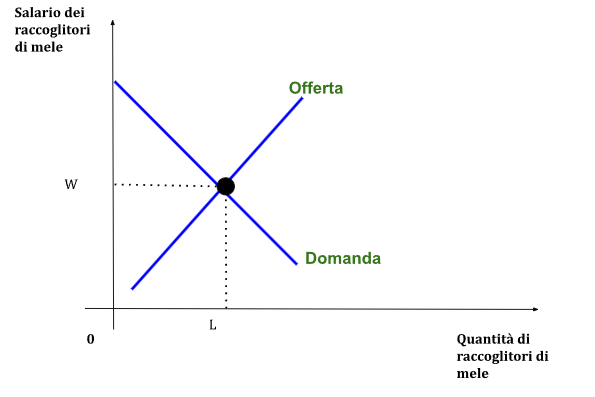
Balances
Suppose we are in a market where there is free competition in terms of both the sale and purchase of labor and that both the price and the wage are given. In this case the company only has to worry about profit maximization.
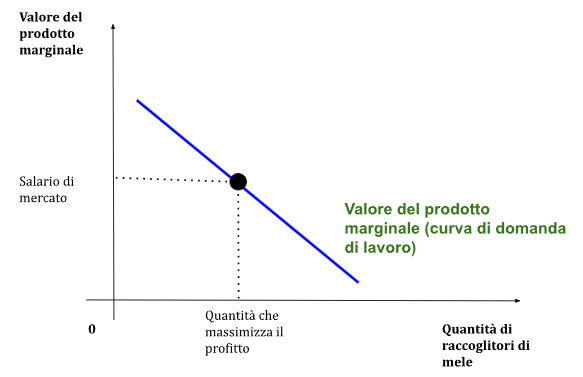
To understand production equilibrium, the following variables will need to be monitored: the production function, the marginal product of labor, the wage and marginal profit.
Marginal Product
In this case the company will have to take into account how much it earns and not how much it produces, therefore it will evaluate how much each worker can produce.
Trade off
We introduce the concept of trade off. The trade off is a certain situation that involves losing or gaining something in order to obtain something else in exchange.
In the labor market the trade off can occur between the exchange of work and free time.
Factor Question
A company under free competition must produce the quantity corresponding to P=C' (price equal to marginal cost)
The company itself determines the quantity of work W=VP'L
Where W = salary
VP'L = Value of marginal product
Note:
VP'L = P x P'L (Product x Marginal Product of Labor)
Making the necessary considerations, even in the labor market we can say that the Price is equal to the marginal cost, i.e. P = C'
Balance graph
Below is the graph of the equilibrium of the labor market
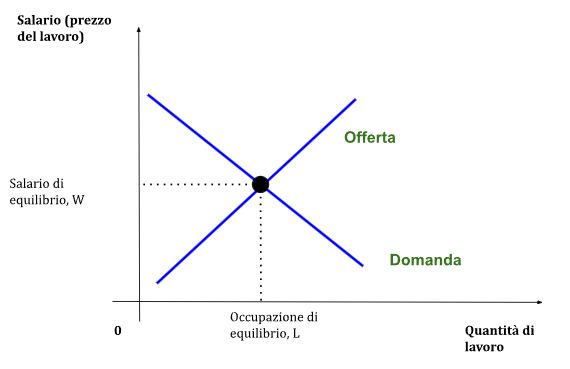
Conclusions
The labor market is based on two main factors, labor and capital.
Request
Have you ever thought about what your best working situation could be? Would you like to have a higher reward or more free time?

ITALIAN
21-04-2024 - Economia - Fattori produttivi [EN]-[IT]
Fattori produttivi
Cenni
Il mercato dei fattori è composto da lavoro e capitale.
In questo mercato l’offerta è l’offerta del lavoro da parte dei lavoratori e la domanda è la domanda di lavoro da parte di datori di lavoro. Il prezzo è il salario.
Nel mercato del lavoro i lavoratori sono liberi di entrare ed uscire quando vogliono, mentre le imprese possono modificare la quantità di lavoro impiegata.
Mercato del lavoro in grafici
Esempio grafico del mercato delle mele

Grafico del mercato dei raccoglitori di mele

Equilibri
Supponiamo di essere in un mercato dove si è in libera concorrenza sia in termini di vendita che di acquisto della manodopera e che sia il prezzo che il salario sono dati. In questo caso l’impresa si deve preoccupare solo della massimizzazione del profitto.
Per capire l’equilibrio di produzione si dovranno monitorare le seguenti variabili: la funzione di produzione, il prodotto marginale del lavoro, il salario e il profitto marginale.
Prodotto marginale
In questo caso l’impresa dovrà tenere conto di quanto guadagna e non di quanto produce, quindi valuterà quanto potrà produrre ogni lavoratore.

Spostamenti
Introduciamo il concetto di trade off. Il trade off è una certa situazione che implica la perdita o il guadagno di qualcosa per ottenere in cambio qualcos’altro.
Nel mercato del lavoro il trade off può avvenire tra lo scambio di lavoro e tempo libero.
Domanda di fattori
Un’impresa in regime di libera concorrenza deve produrre la quantità in corrispondenza di P=C’ (prezzo uguale al costo marginale)
La stessa impresa determina la quantità di lavoro W=VP’L
Dove W = salario
VP’L = Valore del prodotto marginale
Nota:
VP’L = P x P’L (Prodotto x Prodotto marginale del Lavoro)
Facendo le dovute considerazioni, anche nel mercato del lavoro possiamo dire che il Prezzo è uguale al costo marginale, cioè P = C’
Grafico equilibrio
Qui di seguito il grafico dell’equilibrio del mercato del lavoro

Conclusioni
Il mercato del lavoro si basa su due fattori principali, il lavoro ed il capitale.
Domanda
Avete mai pensato a quale potrebbe essere la vostra miglior condizione lavorativa? Vorreste avere una ricompensa più alta o più tempo libero?
THE END