~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
27-02-2024 - Physics - Mass continuity equation [EN]-[IT]
Basic concepts
Thermodynamics is a very broad branch of physics and we can say that even the basic concepts are many. Below are some basic concepts that should always be kept in mind when analyzing a system from a thermodynamic point of view.
Below we explain: Local equilibrium, Eulerian point of view, Lagrangian point of view.
Local equilibrium
A system is in local equilibrium when a small volume consisting of a point is assimilated with its surroundings and will instantly reach equilibrium conditions.
Eulerian point of view
Entering the so-called Eulerian point of view mode means taking a reference space, placing yourself in certain fixed points and observing the particles (for example measuring temperatures), as if we were taking photographs.
Lagrangian point of view
Entering the so-called Lagrangian point of view mode means choosing particles, moving with them and for example measuring their temperature as their position varies.
Mass continuity equation
The continuity equation tells us that if we consider an incompressible fluid flowing in a duct with variable section, due to the law of conservation of mass, the quantity of fluid entering the duct must be equal to the quantity of fluid leaving.
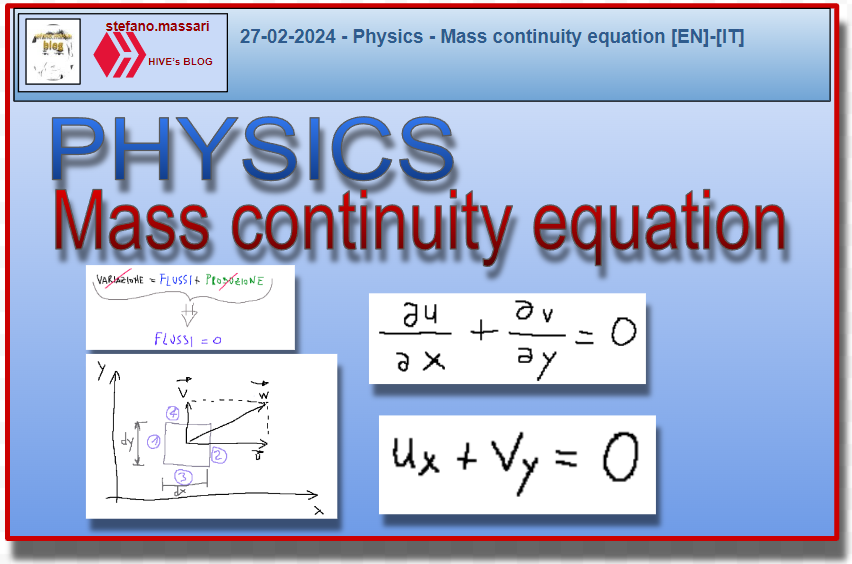
The generic mass balance equation is change = flows + production.
In this case, however, we have two considerations to make
-ρ is constant so the variation is equal to zero
-since we are in stationary regime, production will be zero
So we will have that the mass balance equation will be flows = 0
This concept is described below in the form of a mathematical equation
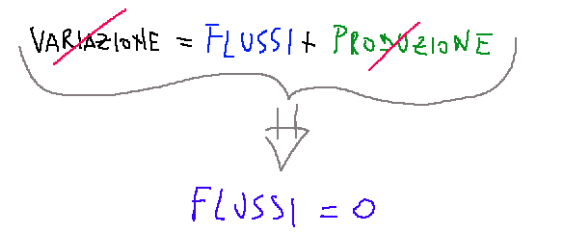
If we consider a generic volume of the fluid we are studying we can represent it as in the graph shown below
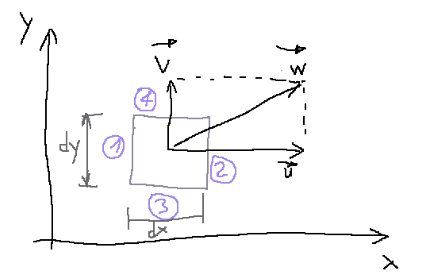
The mass flow through wall 1 is equal to ρ·u·dy·dz
We can now write the following equation considering that we have ρ = constant.
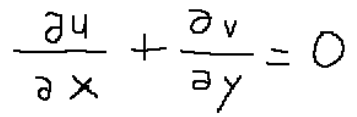
If we were to elaborate the relative partial derivatives we would obtain what was written in the conclusions.
Conclusions
The mass continuity equation looks like this.
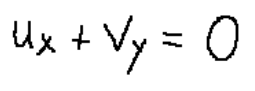
Request
Have you ever tried to do some calculations regarding the mass continuity equation? Have you tried in the past to make calculations regarding the flow rate of a fluid or the section of a duct?

27-02-2024 - Fisica - Equazione di continuità della massa [EN]-[IT]
Concetti base
La termodinamica è un ramo della fisica molto ampio e possiamo dire che anche i concetti base sono tanti. Qui di seguito alcuni concetti base che è bene tenere sempre in mente quando analizziamo un sistema dal punto di vista termodinamico.
Qui di seguito spieghiamo: Equilibrio locale, Punto di vista euleriano, Punto di vista lagrangiano.
Equilibrio locale
Un sistema è in equilibrio locale quando viene assimilato un volumetto costituito da un punto con il suo intorno e si porterà istantaneamente nelle condizioni di equilibrio.
Punto di vista euleriano
Entrare in modalità detta punto di vista euleriano significa prendere uno spazio di riferimento, mettersi in certi punti fissi e osservare le particelle (ad esempio misurare le temperature), come se scattassimo delle fotografie.
Punto di vista lagrangiano
Entrare in modalità detta punto di vista lagrangiano significa scegliere delle particelle, muoversi con esse e ad esempio misurare la loro temperatura al variare della loro posizione.
Equazione di continuità della massa
L’equazione di continuità ci dice che se consideriamo un fluido incomprimibile che scorre in un condotto a sezione variabile, per la legge di conservazione della massa, la quantità di fluido che entra nel condotto deve essere uguale alla quantità di fluido che n esce.
L'equazione generica di bilancio della massa è variazione = flussi + produzione.
In questo caso però abbiamo due considerazioni da fare
-ρ è costante quindi la variazione è uguale a zero
-siccome siamo in regime stazionario la produzione sarà zero
Quindi avremo che l'equazione di bilancio della massa sarà flussi = 0
Qui di seguito viene descritto questo concetto sotto la forma di equazione matematica

Se consideriamo un volumetto generico del fluido che stiamo studiando possiamo rappresentarlo come nel grafico qui sotto mostrato

Il flusso di massa che attraversa la parete 1 è uguale a ρ·u·dy·dz
Possiamo scrivere ora la seguente equazione considerando appunto che abbiamo ρ = costante.
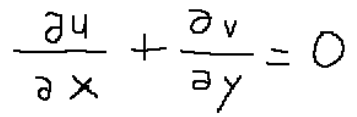
Se andassimo ad elaborare le relative derivate parziali otterremo quanto scritto nelle conclusioni.
Conclusioni
L’equazione di continuità di massa si presenta come segue.
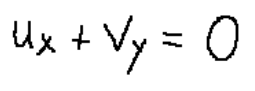
Domanda
Avete mai provato a fare dei calcoli a riguardo dell'equazione di continuità della massa? Avete provato in passato a fare dei calcoli a riguardo della portata di un fluido o della sezione di un condotto?
THE END