~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
02-02-2024 - Physics - The heat transmission equation [EN]-[IT]
The Differential Equation of Heat Transfer by Conduction
Let's quickly clarify two concepts.
Conduction refers to one of the modes of heat transmission between solids.
The thermal conductivity of a material, represented in the formulas with the letter K, is measured in W/m°K.
Thermal conduction, in physics, is the diffusive transport of heat in a solid, liquid or gaseous medium, when two bodies come into contact with each other. It should be noted that this heat transmission occurs between the areas with higher temperatures towards those with lower temperatures.
Initial consideration
Let's take into account that both kinetic and potential energy are equal to zero.
In this case we will have that the total energy corresponds to the internal energy,
The internal energy balance formula is shown below, examining a generic solid.
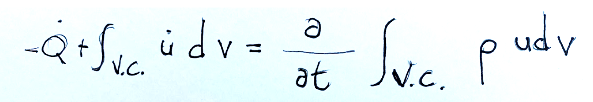
(internal energy balance under certain conditions)
WHERE:
Q = Thermal power which is measured in W. It would be. It would be the heat flow coming out of the solid. Remember that by convention the sign is positive for the heat entering the system.
Integral V.C: udv = possible production of internal energy due to a chemical reaction inside the solid.
By examining various things in which we need the unit flow of heat (Watt/m2), Stokes' theorem and considering the control volume (V.C.) which does not depend on time, we can derive the following formula which is the equation of heat transmission by conduction
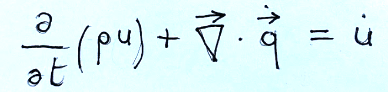
(equation of heat transfer by conduction)
The heat transmission equation by conduction can be rewritten in a simplified way if we consider the following:
-if we consider the equation of state for media considered to have incompressible behavior
-if we consider that the specific heat of the material does not depend on time
-if we consider that for the solid under examination k is practically constant
-if we consider Fourier's law of conduction for a non-isotropic solid
Below is a brief mention of the Fourier equation for flat parts.
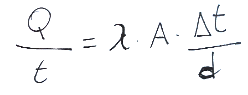
Where:
Q = quantity of heat transferred [J]
t = time [s]
Δt = temperature difference between the two walls [K]
d = wall thickness [m]
λ = thermal conductivity [W / m K]
A = wall surface [m 2]
Having made all the above considerations, the heat transmission equation by conduction can be simplified in the following way.
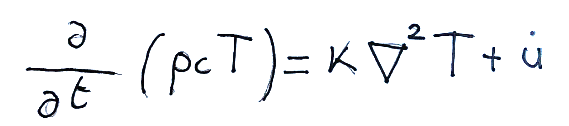

ITALIAN
02-02-2024 - Fisica - L’equazione della trasmissione del calore [EN]-[IT]
L’equazione differenziale della trasmissione del calore per conduzione
Chiariamo in maniera veloce due concetti.
Per conduzione si intende una delle modalità di trasmissione del calore tra solidi.
La conducibilità termica di un materiale, rappresentata nelle formule con la lettera K, si misura in W/m°K.
La conduzione termica, in fisica, è il trasporto diffusivo del calore in un mezzo solido, liquido o aeriforme, nel momento in cui due corpi entrano in contatto tra loro. Si precisa che questa trasmissione del calore avviene tra le zone a temperatura maggiore verso quelle con temperatura minore.
Considerazione iniziale
Teniamo conto che sia l’energia cinetica che quella potenziale siano uguali a zero.
In questo caso avremo che l’energia totale corrisponde all’energia interna,
Qui di seguito è mostrata la formula del bilancio dell’energia interna prendendo in esame un solido generico.
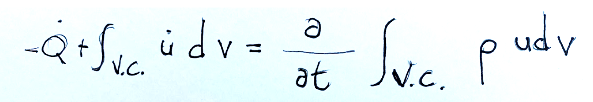
(bilancio dell’energia interna in determinate condizioni)
DOVE:
Q = Potenza termica che si misura in W. Sarebbe. Sarebbe il flusso di calore uscente dal solido. Si ricorda che per convenzione che per il calore entrante nel sistema il segno è positivo.
Integrale V.C: udv = eventuale produzione di energia interna dovuta ad una reazione chimica all’interno del solido.
Andando ad esaminare diverse cose in cui abbiamo bisogno del flusso unitario del calore (Watt/m2), del teorema di Stokes e considerando il volume di controllo (V.C.) che non dipende dal tempo, possiamo ricavare la seguente formula che è l’equazione della trasmissione del calore per conduzione
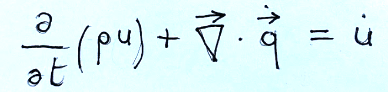
(equazione della trasmissione del calore per conduzione)
L’equazione della trasmissione del calore per conduzione può essere riscritta in maniera semplificata se consideriamo quanto segue:
-se consideriamo l’equazione di stato per i mezzi ritenuti a comportamento incomprimibile
-se consideriamo che il calore specifico del materiale non dipende dal tempo
-se consideriamo che per il solido preso in esame k è praticamente costante
-se consideriamo la legge della conduzione di Fourier per un solido non isotropo
Qui di seguito breve un cenno all'equazione di Fourier per le parti piane.
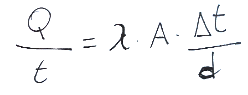
Dove:
Q = quantità di calore trasferita [J]
t = tempo [s]
Δt = differenza di temperatura tra le due pareti [K]
d = spessore della parete [m]
λ = conducibilità termica [W / m K]
A = superficie della parete [m 2]
Fatte tutte le considerazioni di cui sopra, l’equazione della trasmissione del calore per conduzione può essere semplificata nella seguente maniera.
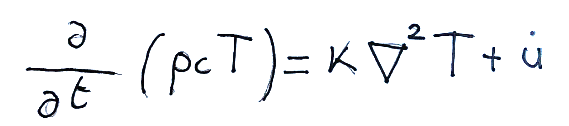
Conclusioni
_
Domanda
_
THE END