~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
04-07-2024 - Energy systems - Single-stage axial turbine[EN]-[IT]
Single-stage axial turbine
The stage of a turbine
A turbine stage consists of a group of components that work together to extract energy from the moving fluid and convert it into mechanical work. Moving energy is typically transmitted by gas or steam.
There are 2 main organs.
1-The distributor, where the thermal potential energy of the fluid is transformed into kinetic energy
2-The impeller where the kinetic energy and the residual thermal potential energy of the fluid are converted into mechanical energy at the shaft.
Each turbine mainly includes two components:
- Stator Blades (or Distributor Blades)
-Rotor Blades (or Rotor Blading)
The stadium - what is it
The stage of a turbine is the assembly of the distributor and the subsequent mobile blades. Remember that the distributor is the stator duct or stator, while the mobile blades are the rotor duct or rotor. A stage can be action-based if the expansion of the fluid occurs in the distributor or it can be reaction-based if the expansion of the fluid occurs both in the distributor and in the impeller.
Classification
Axial action turbines are classified in the following way.
-single action (De Laval)
-with speed jump action (Curtis)
-with pressure jump action (Rateau)
- simple reaction
-multiple expansion reaction (Parsons)
-mixed
Speed Triangles
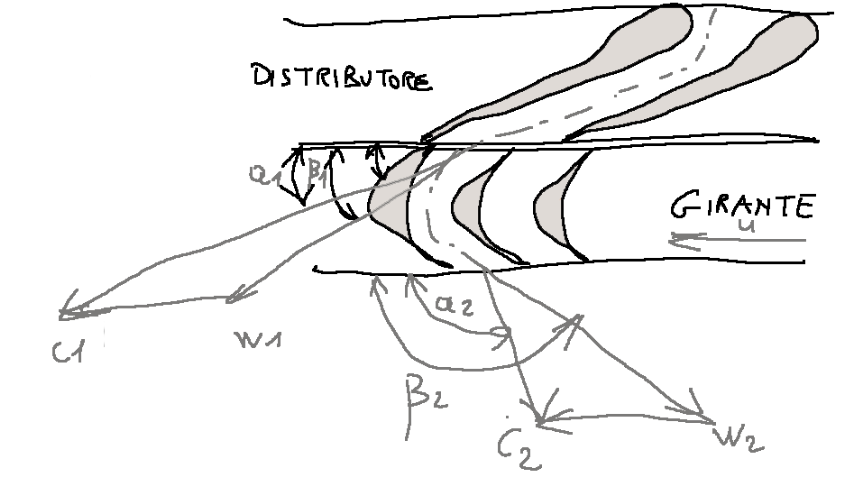
Below is a diagram of what the speed triangles look like in the area of the distributor and the impeller.
Yield
The blading efficiency is expressed as follows.
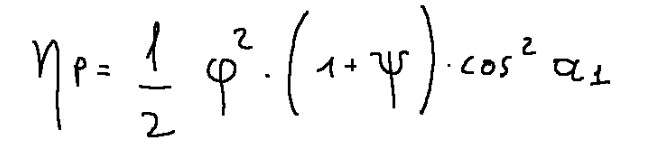
Maximum value
As regards the efficiency of the blading in a De Laval turbine we can say that, assuming characteristic values of the constants (α1=17°, φ=0.95 and ψ=0.92), we have for example a maximum efficiency of 0.76
Conclusions
Turbines are continuous flow driving machines.
Request
Have you ever studied or seen a gas or steam turbine?

ITALIAN
04-07-2024 - Sistemi energetici - Turbina assiale monostadio[EN]-[IT]
Turbina assiale monostadio
Lo stadio di una turbina
Uno stadio di una turbina è costituito da un gruppo di componenti che lavorano insieme per estrarre energia dal fluido in movimento e convertirla in lavoro meccanico. L’energia in movimento viene trasmessa tipicamente da gas o vapore.
Gli organi principali sono 2.
1-Il distributore, dove l’energia potenziale termica del fluido viene trasformata in energia cinetica
2-La girante dove l’energia cinetica e l’energia potenziale termica residua del fluido vengono convertite in energia meccanica all’albero.
Ogni turbina comprende principalmente due componenti:
-Pale Statoriche (o Palettatura del Distributore)
-Pale Rotoriche (o Palettatura del Rotore)
Lo stadio - cosa è
Lo stadio di una turbina è l’insieme del distributore e della successiva palettatura mobile. Ricordiamo che il distributore è il condotto statorico o statore ,mentre la palettatura mobile è il condotto rotorico o rotore. Uno stadio può essere ad azione se l’espansione del fluido avviene nel distributore oppure può essere a reazione se l’espansione del fluido avviene sia nel distributore che nella girante.
Classificazione
Le turbine assiali ad azione si classificano nella seguente maniera.
-ad azione semplice (De Laval)
-ad azione a salti di velocità (Curtis)
-ad azione a salti di pressione (Rateau)
-a reazione semplice
-a reazione ad espansioni multiple (Parsons)
-miste
Triangoli delle velocità
Qui si seguito uno schema di come sono i triangoli delle velocità nella zona del distributore e della girante.

Rendimento
Il rendimento della palettatura è espresso come segue.
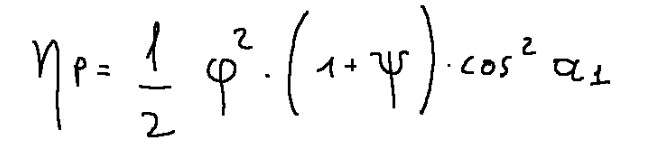
Valore massimo
Per quanto riguarda il rendimento della palettatura in una turbina De Laval possiamo dire che, assumendo valori caratteristici delle costanti (α1=17°, φ=0.95 e ψ=0.92), si ha ad esempio un rendimento massimo di 0.76
Conclusioni
Le turbine sono macchine motrici a flusso continuo.
Domanda
Avete mai studiato o visto una turbina a gas o a vapore?
THE END