Array manipulation refers to changing the shape, size and content of array. In this post, we will see some of the commonly used array manipulation functions and techniques using NumPy library. NumPy library is the best when doing numerical data analysis and scientific computing that relies on array and its operation. The first manipulation operation is reshaping the array. NumPy allows us to reshape the array without changing the content on the array.
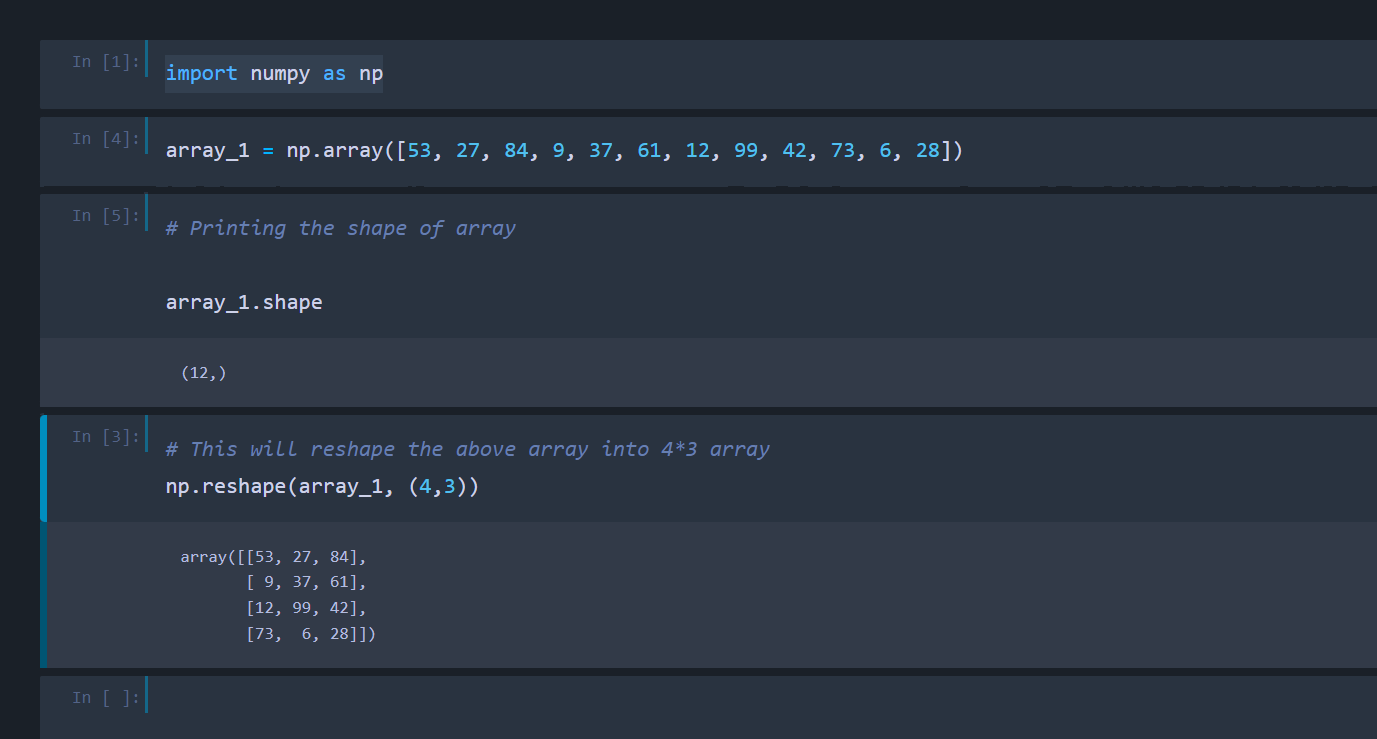
In the following example we defined a one-dimensional array containing 12 elements. We then reshaped it into array containing 4 rows and 3 columns.
import numpy as np
array_1 = np.array([53, 27, 84, 9, 37, 61, 12, 99, 42, 73, 6, 28])
# Printing the shape of array
array_1.shape
# This will reshape the above array into 4*3 array
np.reshape(array_1, (4,3))
You can see the output as below:
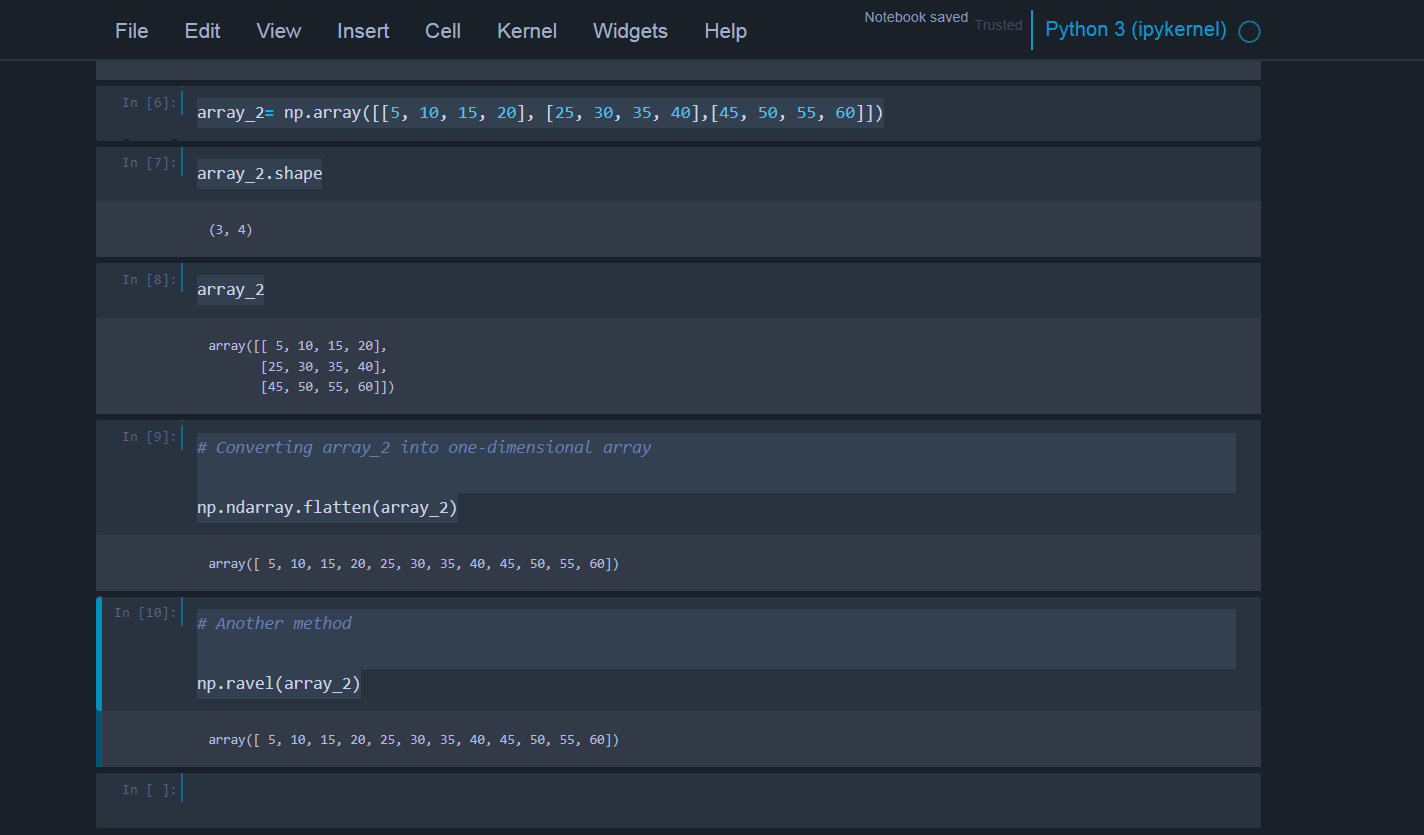
Next we will see reshaping the two dimensional array into one dimensional array. We can do this by using flatten() and ravel() function. Both of them do exactly the same task but there is a slight difference between these two methods. Flatten returns a copy of array thus occupy memory whereas ravel returns only the view of the array and doesn't occupy the memory and is faster than flatten. This is particularly useful when there is a thousands of data to work with. We will see its usage with example below:
array_2= np.array([[5, 10, 15, 20], [25, 30, 35, 40],[45, 50, 55, 60]])
array_2.shape
array_2
# Converting array_2 into one-dimensional array
np.ndarray.flatten(array_2)
# Another method
np.ravel(array_2)
We can see the output as below after executing the code:
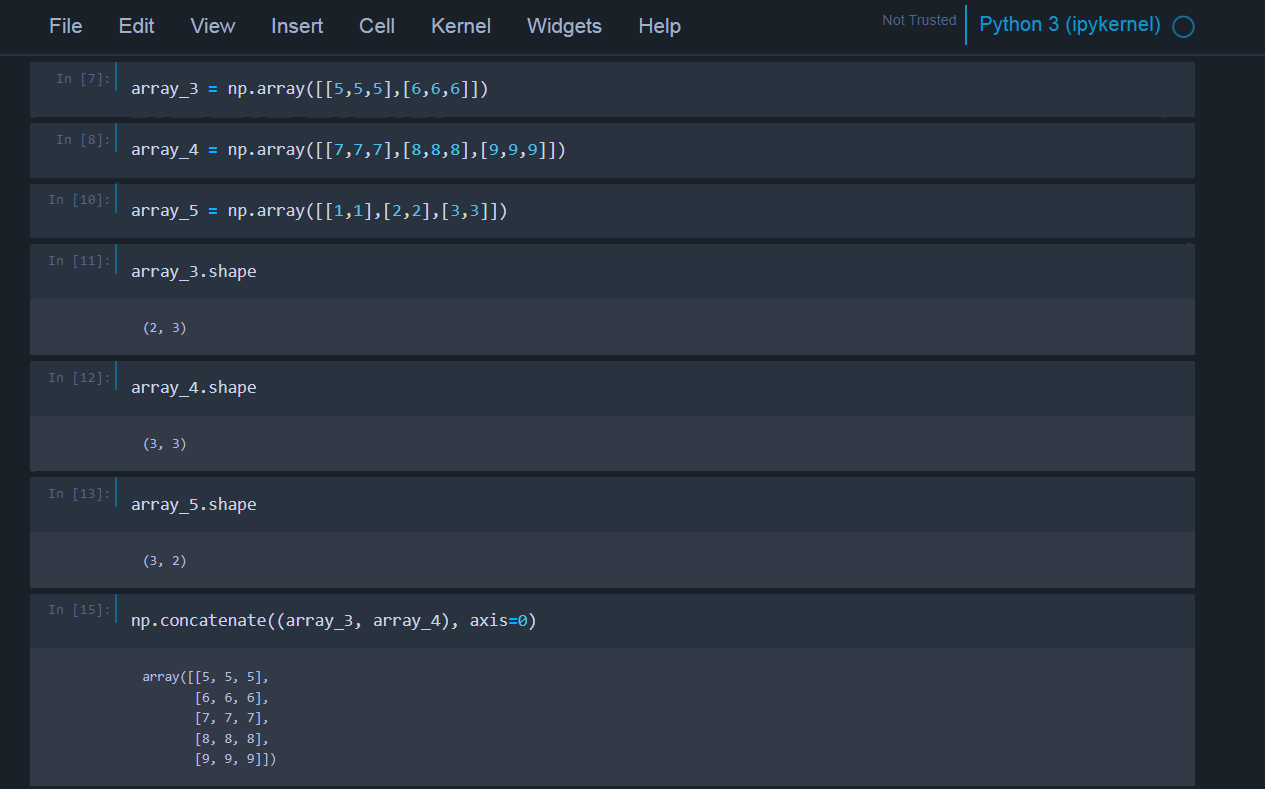
Next we will see another important array operation which is concatenation. It is used to merge two or more arrays into one. If you are concatenating arrays across the rows you need to make sure that both of the arrays must have same number of column and vice-versa for the column. The following is a simple program to concatenate two arrays along row(axis=0).
array_3 = np.array([[5,5,5],[6,6,6]])
array_4 = np.array([[7,7,7],[8,8,8],[9,9,9]])
array_5 = np.array([[1,1],[2,2],[3,3]])
array_3.shape
array_4.shape
array_5.shape
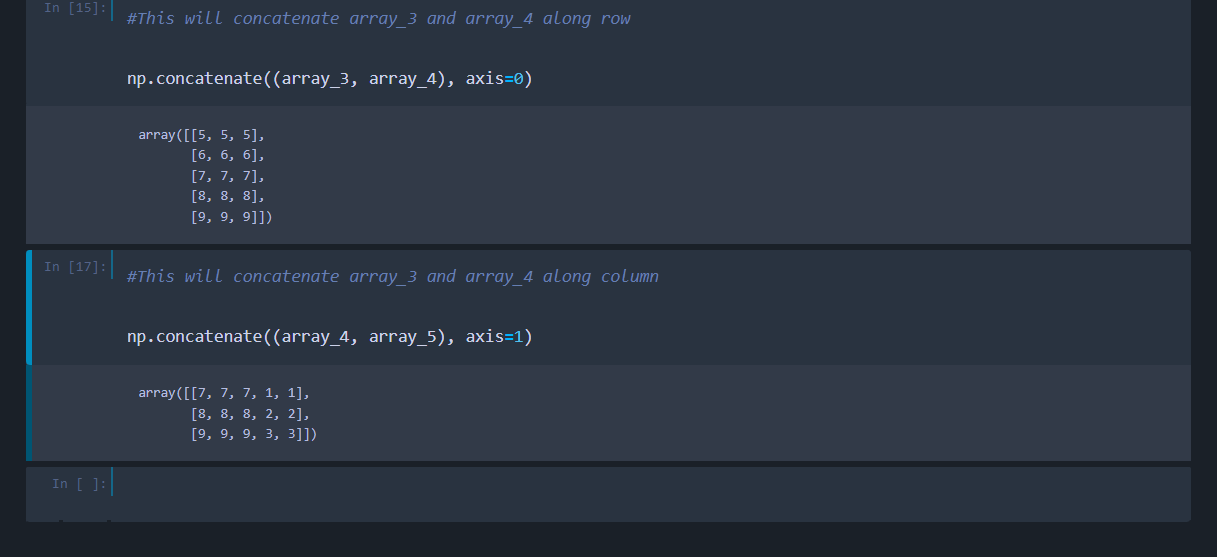
# This will concatenate array_3 and array_4 along row
np.concatenate((array_3, array_4), axis=0)
If you run the above code, you will get the following output.
Similarly we can concatenate array_4 and array_5 along the vertical axis by specifying axis=1(column).
#This will concatenate array_3 and array_4 along column
np.concatenate((array_4, array_5), axis=1)
The output will be as below:
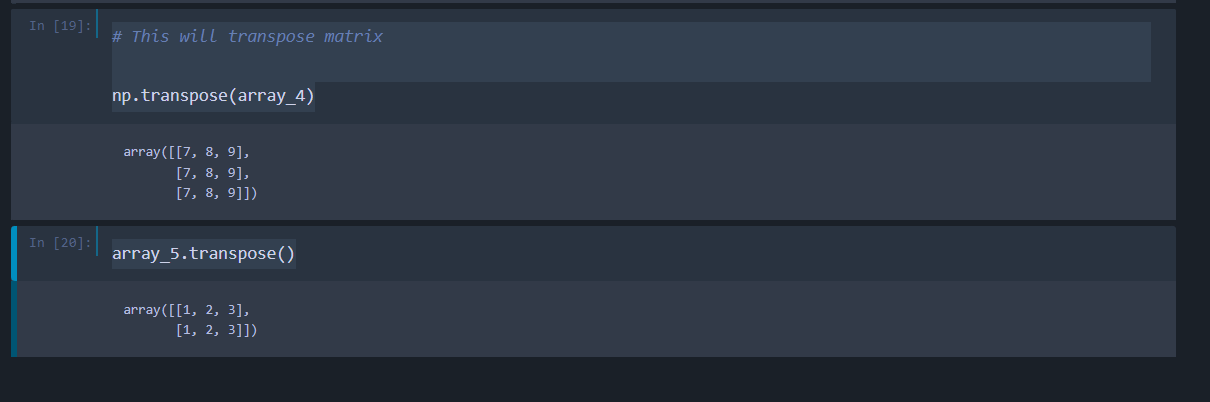
Next we will be transposing an array. Transposing simply means interchanging the value of rows and columns. It is very simple to do.
# This will transpose matrix
np.transpose(array_4)
# or
array_5.transpose()
You will get the output as below:
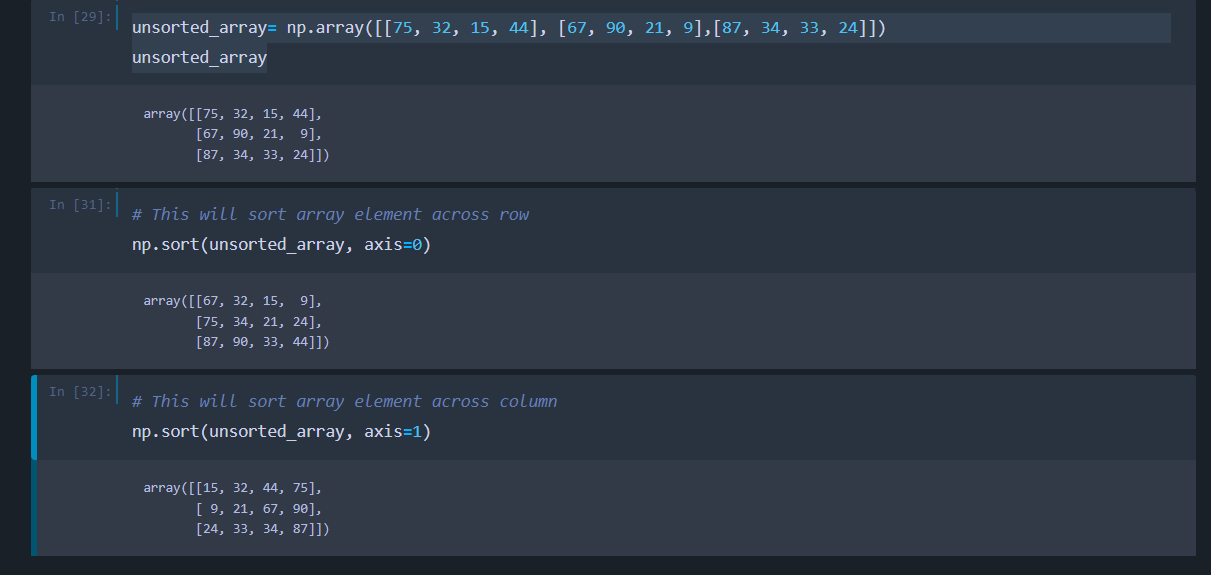
At last we will be seeing about sorting elements inside an array both vertically and horizontally.
# This will sort array element across row
np.sort(unsorted_array, axis=0)
# This will sort array element across column
np.sort(unsorted_array, axis=1)
If you execute the above code, it will show the following output. Remember that, Axis = 0 represents operations along the rows and axis=1 represents operations along the column