Bus Bars and Cabling
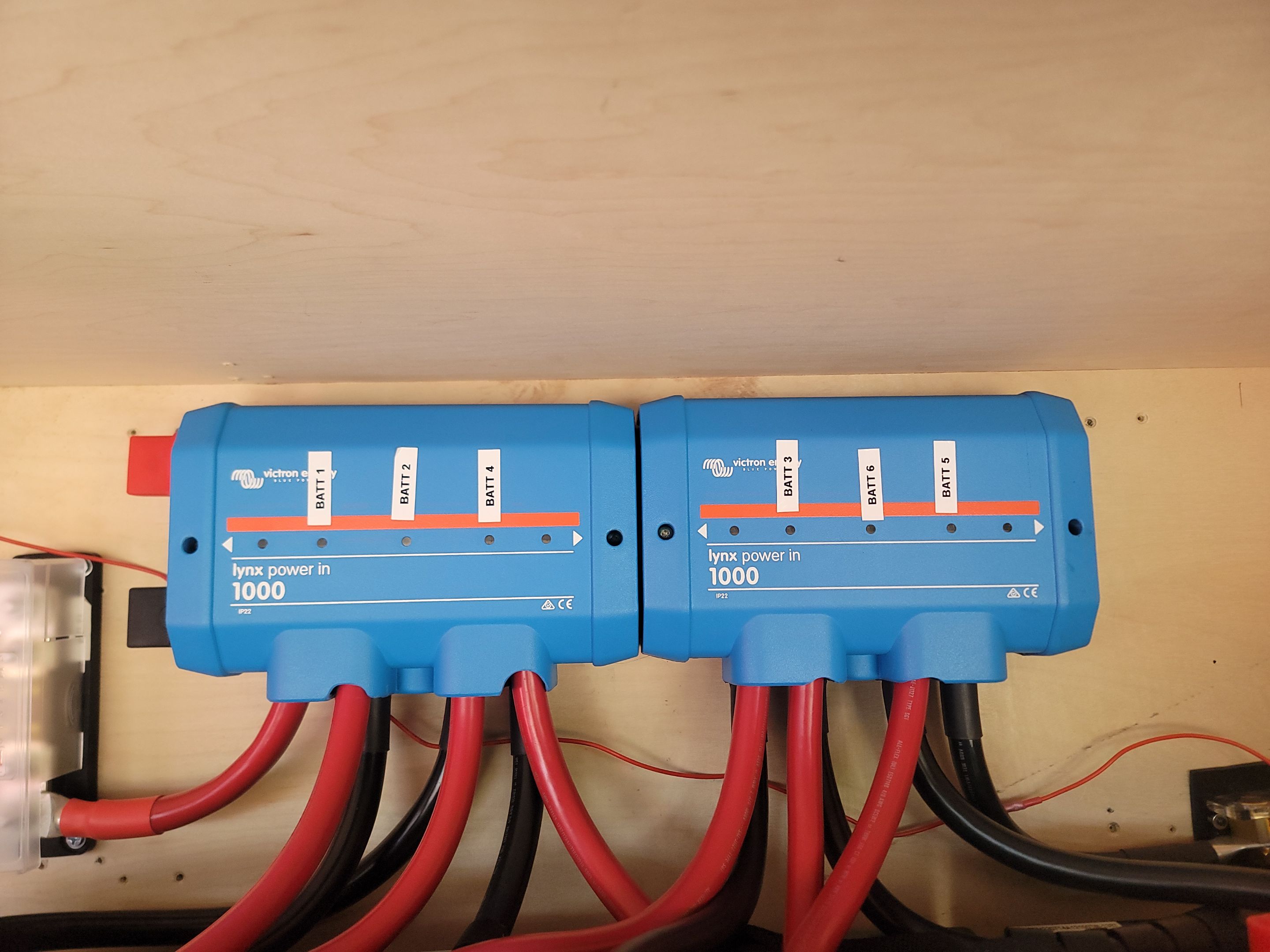
These are two 1000-amp bus bars connecting the batteries together in parallel. This setup provides a total of 600 amp-hours of capacity. Unlike lead-acid batteries, LiFePO4 batteries can be discharged down to empty without causing any damage. This deep discharge capability makes them much more efficient and reliable for extended use.
The batteries are connected to the bus bars using 4/0 electrical cables. Each cable is of identical length to ensure proper balancing of the batteries. Equal cable lengths are crucial because they ensure that each battery shares the load evenly, preventing any single battery from being overworked and potentially damaged. The 4/0 cables are very thick, offering minimal resistance and ensuring maximum voltage transfer from the battery bank.
The thickness of the 4/0 cables, which is approximately 0.46 inches in diameter, is designed to handle high current loads with minimal voltage drop. This is particularly important in high-capacity battery setups where efficiency and safety are paramount. The heavy-duty cables also help in reducing heat buildup, which can be a concern in systems with high current flow.
To accommodate the thick cables, I had to modify the covers slightly. This involved cutting the covers to allow the cables to be routed properly to the batteries. Ensuring that the cables were securely and safely connected was a top priority, as loose or poorly connected cables can lead to inefficiencies and pose safety risks.
Here's a detailed breakdown of the setup and its benefits:
Bus Bars: The two 1000-amp bus bars are critical components that distribute power evenly across the battery bank. By connecting the batteries in parallel, the bus bars ensure that the total capacity of 600 amp-hours is available for use. These bus bars are robust enough to handle the high current without overheating or becoming damaged.
4/0 Electrical Cables: The use of 4/0 cables, also known as quadruple aught cables, is essential for minimizing resistance and ensuring efficient power transfer. These cables are rated to handle very high currents, which is necessary for the high-capacity LiFePO4 battery bank.
Identical Cable Lengths: Maintaining equal lengths for all the cables ensures that the electrical resistance is uniform across the system. This uniformity is crucial for balancing the load among all the batteries, preventing any one battery from being overburdened.
Cable Routing and Modifications: Proper cable management not only ensures safety but also enhances the overall efficiency of the electrical system. For this deployment I have the positive of the battery bank on one side of the bus bar, and the negative on the other. This ensures all power drawn from the battery bank will flow across the entire bus bar.
Deep Discharge Capability: One of the significant advantages of LiFePO4 batteries over lead-acid batteries is their ability to be fully discharged without damage. This feature maximizes the usable capacity of the batteries, providing more available power compared to lead-acid batteries, which should not be discharged beyond 50% of their capacity.
Overall, this setup with 1000-amp bus bars and 4/0 cables has significantly improved the efficiency, reliability, and safety of my trailer's power system. The ability to utilize the full capacity of the LiFePO4 batteries, coupled with the robust and well-balanced electrical connections, ensures that I have a dependable power source for all my needs while on the road.
Note: I wrote the initial paragraphs and then enhanced them with the help of ChatGPT.