 source
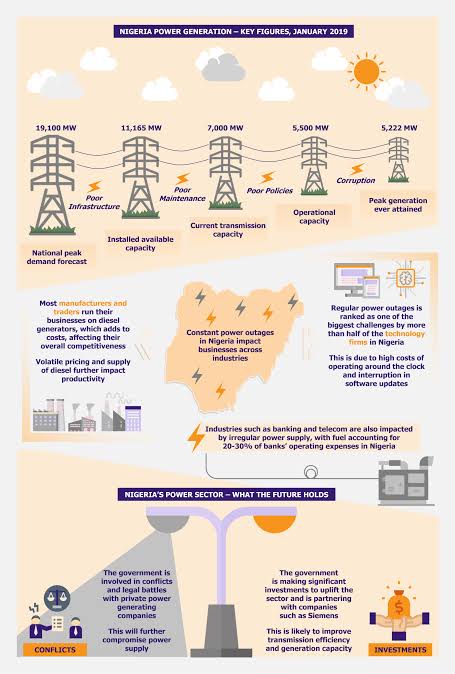
source According to NairaMetrics, Nigeria's power generation peaked at 4,594.6MW as of November 2022. The electricity generated is considerably low considering the country's population of over 250 million people. Despite having a generating capacity of 22,000 megawatts, Nigeria has failed abysmally to supply electricity to its citizens leading to severe truncation of development.
A feasible power generation capacity for Nigeria depends on various factors such as population growth, industrial development, energy demand projections, available resources, and technological advancements. Currently, Nigeria's installed electricity generation capacity is around 13,000 megawatts (MW), but actual generation often falls short of this due to infrastructure challenges, fuel supply constraints, and inefficiencies in the power sector.
%20(11).jpeg) source
source To determine a realistic and sustainable power generation capacity for Nigeria, it's essential to consider the following:
Demand Projections: Analyzing future electricity demand based on population growth, urbanization trends, industrial expansion, and increasing electrification in rural areas.
Resource Availability: Assessing the country's energy resources, including fossil fuels (such as natural gas and coal), renewable sources (such as solar, wind, hydro, and biomass), and potential for energy efficiency measures.
Infrastructure Development: Investing in power generation infrastructure, transmission grids, and distribution networks to ensure reliable electricity supply across the country.
Technological Innovation: Leveraging advancements in power generation technologies, such as combined-cycle gas turbines, renewable energy systems, energy storage solutions, and smart grid technologies, to optimize efficiency and reliability.
Policy and Regulatory Framework: Implementing supportive policies, regulatory reforms, and incentive mechanisms to attract private investment, promote competition, and ensure transparency and accountability in the power sector.
Environmental Considerations: Balancing energy security and economic development with environmental sustainability by prioritizing cleaner and renewable energy sources, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and mitigating the impact of power generation on air and water quality.
%20(10).jpeg) source
source Based on these considerations, a feasible power generation capacity for Nigeria could range from 50,000 MW to 100,000 MW over the next decade, with a significant emphasis on diversifying the energy mix, promoting renewable energy deployment, and enhancing energy efficiency measures. This capacity expansion should be accompanied by investments in transmission and distribution infrastructure, regulatory reforms to attract private sector participation, and concerted efforts to address operational challenges and systemic inefficiencies in the power sector.
Ultimately, achieving a feasible and sustainable power generation capacity for Nigeria requires a holistic approach that integrates technological innovation, policy support, financial investment, and stakeholder collaboration to meet the country's growing energy needs, drive economic growth, and improve the quality of life for its citizens.
Generating and distributing over 10,000 gigawatts of electricity to Nigeria's population of approximately 250 million people is an ambitious goal that requires careful planning, investment, and implementation. To achieve this objective, the federal government must prioritize various strategies that address generation capacity, transmission infrastructure, distribution networks, and renewable energy sources. Let's explore some detailed approaches to accomplish this monumental task:
1. Investment in Power Plants:
- The federal government should attract both domestic and foreign investment to build a diverse portfolio of power plants, including coal, natural gas, hydroelectric, solar, wind, and geothermal facilities.
- Public-private partnerships (PPPs) can be utilized to fund the construction of large-scale power plants, leveraging both government resources and private sector expertise.
2. Renewable Energy Integration:
- Promoting the development of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind is essential for sustainable electricity generation.
- Incentives, subsidies, and tax breaks can encourage businesses and individuals to invest in rooftop solar panels and small-scale wind turbines, contributing to decentralized power generation.
3. Upgrade Transmission Infrastructure:
- Modernizing and expanding the country's transmission infrastructure is critical for efficiently transporting electricity from power plants to distribution networks.
- Investment in high-voltage transmission lines, substations, and grid automation technologies can enhance reliability and reduce transmission losses.
4. Strengthen Distribution Networks:
- Addressing technical losses, theft, and inefficiencies in distribution networks is essential for ensuring that generated electricity reaches end-users.
- Deploying smart meters, implementing metering infrastructure, and enhancing monitoring and enforcement mechanisms can improve revenue collection and network performance.
5. Energy Storage Solutions:
- Deploying energy storage systems such as battery storage and pumped hydro storage can help address intermittency issues associated with renewable energy sources.
- These storage solutions can store excess electricity during periods of low demand and discharge it during peak demand hours, ensuring a reliable and stable power supply.
6. Rural Electrification Initiatives:
- Implementing rural electrification programs is crucial for extending access to electricity to underserved communities.
- Off-grid and mini-grid solutions powered by renewable energy sources can provide reliable electricity to remote areas where grid extension is not feasible.
7. Regulatory Reforms:
- Streamlining regulatory processes, reducing bureaucratic hurdles, and ensuring a transparent and conducive business environment are essential for attracting investment in the power sector.
- Enforcing regulations, combating corruption, and improving governance can enhance accountability and efficiency in the electricity supply chain.
8. Capacity Building and Training:
- Investing in workforce development, training programs, and technical education can build a skilled workforce capable of operating and maintaining power infrastructure.
- Collaboration with universities, vocational schools, and training institutions can ensure a steady pipeline of talent for the power sector.
9. Public Awareness and Engagement:
- Educating the public about the importance of energy conservation, efficient usage, and sustainability can promote responsible energy consumption habits.
- Engaging with communities, stakeholders, and civil society organizations can foster support for energy projects and initiatives.
10. International Cooperation and Partnerships:
- Collaborating with international organizations, development banks, and donor agencies can provide financial assistance, technical expertise, and best practices for power sector development.
- Participating in regional initiatives and intergovernmental partnerships can enhance cross-border energy trade and cooperation.
11. Energy Efficiency Programs:
- Implementing energy efficiency measures and initiatives can reduce overall electricity demand, easing pressure on the power generation and distribution systems.
- Encouraging the adoption of energy-efficient appliances, lighting, and industrial processes through incentives, labeling schemes, and public awareness campaigns can result in significant energy savings.
12. Community Engagement and Ownership:
- Engaging local communities in energy projects fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility, leading to better acceptance and sustainability of initiatives.
- Establishing community-based energy cooperatives or partnerships can empower residents to participate in decision-making, investment, and management of energy infrastructure.
- Promoting decentralized energy solutions, such as mini-grids and off-grid systems, allows communities to meet their energy needs autonomously, improving resilience and energy access in remote areas.
- Providing training and capacity-building programs for community members on energy management, maintenance, and entrepreneurship can create job opportunities and economic empowerment at the grassroots level.
- Encouraging community-led initiatives for renewable energy deployment, such as solar microgrids or biogas digesters, can unlock local resources and reduce dependency on centralized power systems.
13. Research and Development Investment:
- Investing in research and development (R&D) efforts is essential for driving innovation, improving technology efficiency, and discovering new solutions for energy generation, storage, and distribution.
- Collaborating with universities, research institutions, and private sector partners to fund R&D projects focused on renewable energy, smart grid technologies, energy storage systems, and advanced materials can accelerate progress towards sustainable energy goals.
- Establishing innovation hubs, incubators, and technology parks dedicated to energy innovation can foster collaboration, knowledge exchange, and commercialization of research findings.
- Supporting technology demonstration projects and pilot initiatives allows for real-world testing and validation of new energy technologies before scaling up to full deployment.
- Creating incentives and funding mechanisms, such as grants, tax credits, and venture capital investments, encourages private sector engagement in energy innovation and entrepreneurship.
14. International Collaboration and Partnerships:
- Engaging in international collaboration and partnerships enables knowledge sharing, technology transfer, and access to financial resources and expertise from global stakeholders.
- Participating in multilateral initiatives, such as the United Nations Sustainable Energy for All (SEforALL) program or the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), provides opportunities for capacity building, policy dialogue, and coordinated action on energy issues.
- Forming strategic partnerships with other countries, development agencies, and international organizations facilitates access to funding, investment opportunities, and technical assistance for energy projects.
- Leveraging bilateral agreements and diplomatic channels strengthens cooperation on energy security, climate change mitigation, and sustainable development goals at the regional and global levels.
- Engaging with international financial institutions, such as the World Bank, African Development Bank, and regional development banks, helps mobilize financing for large-scale energy infrastructure projects and policy reforms.
15. Monitoring, Evaluation, and Learning:
- Establishing robust monitoring, evaluation, and learning (MEL) mechanisms is crucial for tracking progress, assessing impact, and identifying lessons learned in energy sector interventions.
- Developing performance indicators, benchmarks, and targets allows for regular monitoring and evaluation of energy projects' outcomes and effectiveness.
- Conducting periodic reviews, assessments, and impact evaluations helps identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement in energy policies, programs, and projects.
- Promoting knowledge sharing, peer learning, and best practice dissemination among stakeholders fosters continuous improvement and innovation in energy sector governance and management.
- Integrating MEL frameworks into energy planning, budgeting, and decision-making processes ensures evidence-based policymaking and resource allocation for sustainable energy development.
%20(12).jpeg) source
source Conclusion:
Overall, implementing these strategies can contribute to building a more resilient, inclusive, and sustainable energy sector in Nigeria. By prioritizing renewable energy deployment, enhancing energy efficiency, fostering community engagement, investing in research and development, leveraging international collaboration, and strengthening monitoring and evaluation efforts, Nigeria can unlock its vast energy potential and accelerate progress towards achieving universal energy access, economic growth, and environmental sustainability. However, realizing these goals requires strong political will, effective governance, adequate financing, and concerted efforts from all stakeholders, including government agencies, private sector actors, civil society organizations, and local communities. By working together and embracing innovation and change, Nigeria can overcome its energy challenges and create a brighter and more prosperous future for all its citizens.
#nigeria #development #electricity #naija #renewableenergy #energyaccess #sustainabledevelopment #energyinfrastructure #communityengagement #researchanddevelopment #internationalcollaboration #energyefficiency #monitoringandevaluation #sustainableenergysolutions #energyinnovation #climatechangemitigation #economicgrowth #environmentalsustainability
Written by @Ukeme Uduak