[ESP]
¡Hola, queridos amigos y comunidad de Hive! 🌟
Hoy quiero compartir con ustedes un ejercicio fascinante: resolver un circuito mixto de resistencias en forma de cubo. Este tipo de problema es excelente para aplicar nuestras habilidades en las leyes de Ohm y Kirchhoff. 🚀
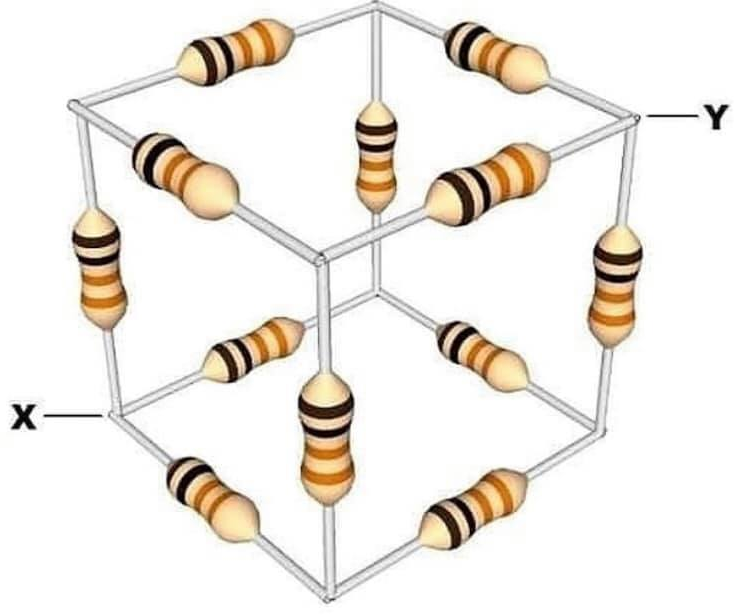
El Desafío: Un Cubo de Resistencias 📦🔧
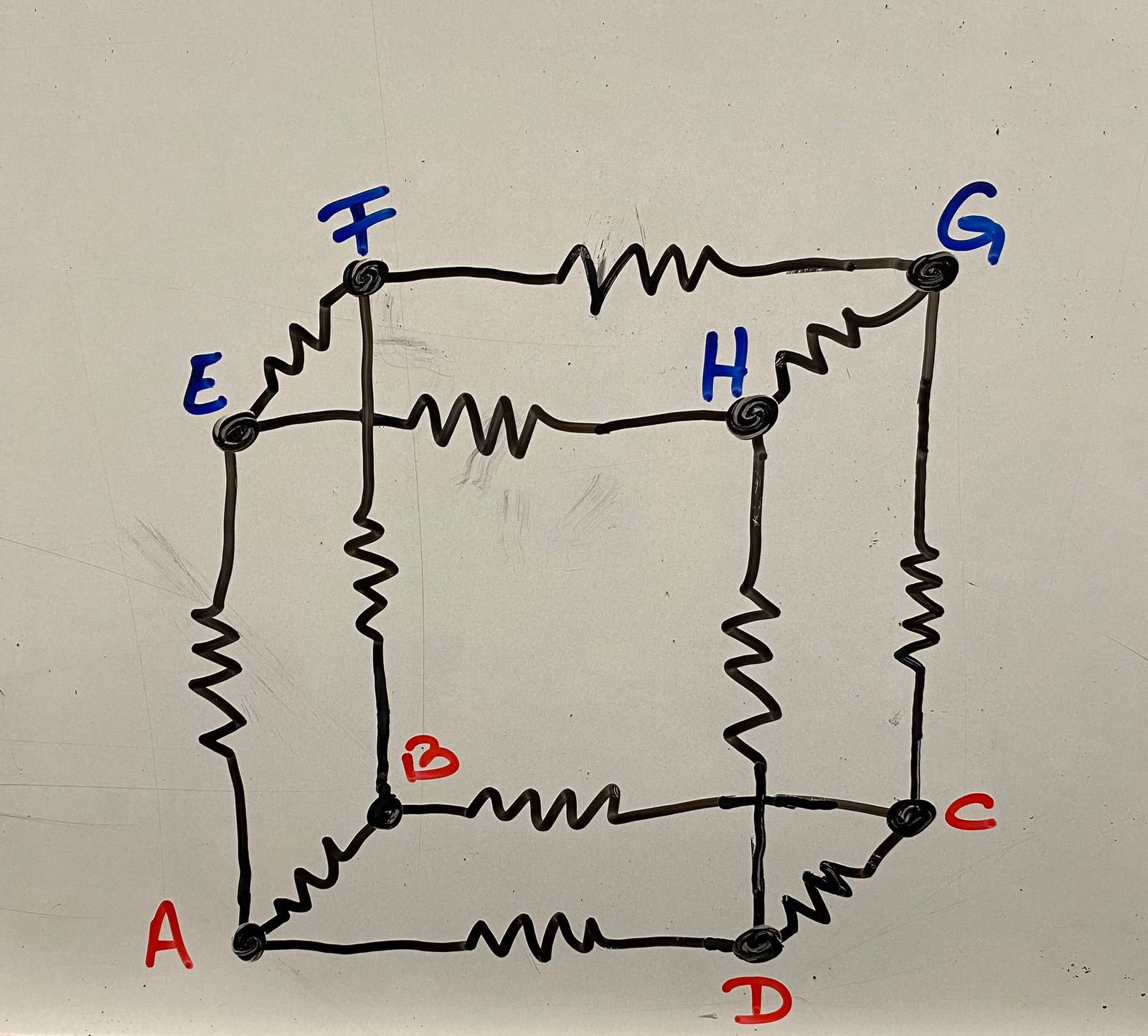
Imaginemos un cubo donde cada arista representa una resistencia de 1000 Ohms. La tensión se aplica entre dos vértices opuestos del cubo, es decir, entre dos vértices más lejanos. Nuestro objetivo es calcular las caídas de tensión y las corrientes en cada rama del cubo.
Paso 1: Entender la Configuración del Cubo 🧠
Primero, visualicemos el cubo y etiquetemos los vértices para tener una referencia clara:
- Vértices A, B, C, D en la base.
- Vértices E, F, G, H en la parte superior.
Las aristas (resistencias) son:
- AB, BC, CD, DA en la base.
- EF, FG, GH, HE en la parte superior.
- AE, BF, CG, DH verticales.
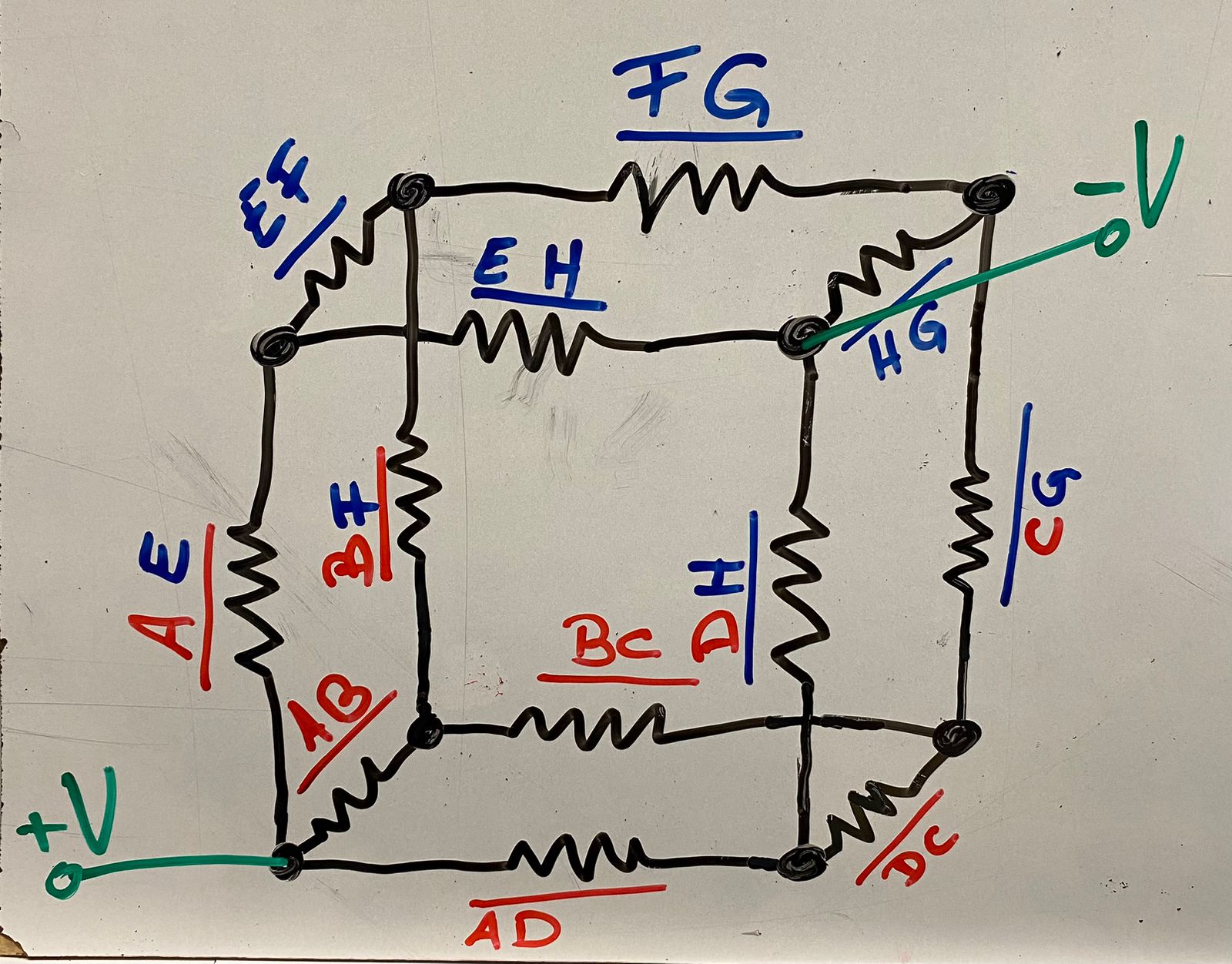
La tensión se aplica entre los vértices A y H.
Paso 2: Aplicar la Ley de Ohm y Kirchhoff 📏🔋
Ley de Kirchhoff de Corrientes (LKC) 🔄
Según la LKC, la suma de las corrientes que entran en un nodo es igual a la suma de las corrientes que salen del nodo.Ley de Kirchhoff de Tensiones (LKT) 🔄
Según la LKT, la suma algebraica de las diferencias de potencial en cualquier lazo cerrado es igual a cero.
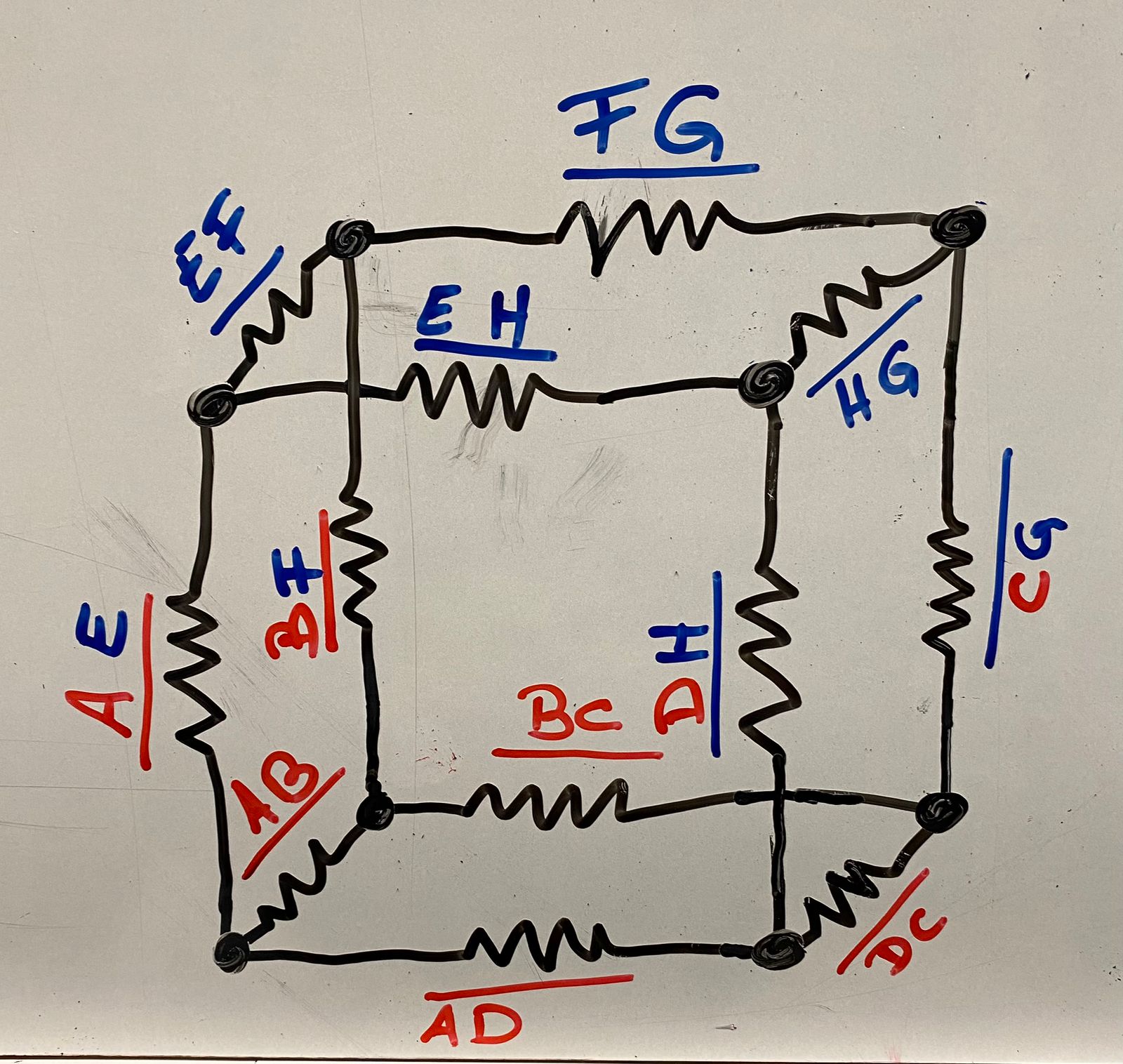
Paso 3: Identificar los Nodos y Lazos 🕵️♂️🔍
Identifiquemos los nodos principales y los lazos relevantes:
- Nodos: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H.
Lazos principales para aplicar LKT.
Paso 4: Establecer las Ecuaciones de Corriente 📊
Para cada nodo, aplicamos la LKC. Considerando la simetría del cubo, podemos simplificar nuestro análisis.
Nodo A: 𝐼𝐴𝐸 =𝐼𝐴𝐵 + 𝐼𝐴𝐷
Nodo H: 𝐼𝐻𝐸 + 𝐼𝐻𝐹 + 𝐼𝐻𝐺 = 𝐼𝑡
Paso 5: Establecer las Ecuaciones de Tensión 📉
Para los lazos, aplicamos la LKT. Esto nos permitirá encontrar las caídas de tensión y relacionarlas con las corrientes.
Lazo A-B-F-H-E: 𝑉=𝐼𝐴𝐵.𝑅 + 𝐼𝐵𝐹.𝑅 + 𝐼𝐹𝐻.𝑅 + 𝐼𝐻𝐸.𝑅
Lazo A-D-H-E: 𝑉=𝐼𝐴𝐷.𝑅 + 𝐼𝐷𝐻.𝑅 + 𝐼𝐻𝐸.𝑅
Paso 6: Resolver el Sistema de Ecuaciones 🧮
Ahora, resolvemos el sistema de ecuaciones para encontrar las corrientes en cada rama. Debido a la simetría, podemos considerar que algunas corrientes son iguales. Esto simplifica las ecuaciones.
Corrientes en Resistencias Equivalentes:
La corriente total 𝐼𝑡 se distribuye a través de las resistencias de manera simétrica. Calculamos la resistencia equivalente 𝑅𝑒𝑞
𝑅𝑒𝑞=5/6.𝑅
Con 𝑅=1000Ω
𝑅𝑒𝑞=5/6 . 1000Ω = 833.33 Ω
Usamos la Ley de Ohm para encontrar la corriente total 𝐼𝑡:
𝐼𝑡 = 𝑉/𝑅𝑒𝑞 = 𝑉/833.33 Ω
Paso 7: Calcular Caídas de Tensión y Corrientes en Cada Rama ⚙️
Para cada resistencia individual, calculamos la caída de tensión usando 𝑉 = 𝐼.𝑅 . Considerando la corriente total y la distribución uniforme, calculamos las corrientes en cada rama.
Ejemplo de Cálculo:
Supongamos que la tensión aplicada 𝑉 es 10V:
𝐼𝑡 = 10𝑉/833.33Ω ≈ 0.012𝐴
Distribuyendo la corriente entre las resistencias en paralelo:
𝐼𝐴𝐸 = 𝐼𝐴𝐷 = 𝐼𝐴𝐵 = 𝐼𝐻𝐸 = 𝐼𝐻𝐹 = 𝐼𝐻𝐺 ≈ 0.002𝐴
Paso 8: Verificación de Resultados ✔️
Finalmente, verificamos los resultados sumando las caídas de tensión en los lazos cerrados y asegurándonos de que cumplan con la LKT. Esto nos da la certeza de que nuestros cálculos son correctos.
Resumen 📝
Resolver un circuito mixto de resistencias en forma de cubo puede parecer complicado al principio, pero aplicando sistemáticamente las leyes de Ohm y Kirchhoff, podemos descomponer el problema y encontrar una solución precisa.
Espero que este ejercicio haya sido tan interesante para ustedes como lo fue para mí. ¡No duden en comentar sus preguntas o experiencias similares resolviendo circuitos complejos!
Ojala que esta explicación detallada sea útil para todos los entusiastas de la electrónica y los circuitos en la comunidad de Hive.
¡Hasta el proximo post! 🚀⚡️
[ENG]
Hello, dear friends and Hive community! 🌟
Today I want to share with you a fascinating exercise: solving a mixed resistance circuit in the shape of a cube. This type of problem is great for applying our skills in Ohm's and Kirchhoff's laws. 🚀
The Challenge: A Cube of Resistances 📦🔧
Let's imagine a cube where each edge represents a resistance of 1000 Ohms. The tension is applied between two opposite vertices of the cube, that is, between two furthest vertices. Our goal is to calculate the voltage drops and currents in each branch of the cube.
Step 1: Understanding the Cube Configuration 🧠
First, let's visualize the cube and label the vertices for a clear reference:
- Vertices A, B, C, D at the base.
- Vertices E, F, G, H at the top.
The edges (resistances) are:
- AB, BC, CD, DA at the base.
- EF, FG, GH, HE at the top.
- AE, BF, CG, DH vertical.
The tension is applied between vertices A and H.
Step 2: Apply Ohm and Kirchhoff's Law 📏🔋
Kirchhoff's Law of Currents (LKC) 🔄
According to the LKC, the sum of the currents entering a node is equal to the sum of the currents leaving the node.Kirchhoff's Stress Law (LKT) 🔄
According to the LKT, the algebraic sum of the potential differences in any closed loop is equal to zero.
Step 3: Identify the Nodes and Ties 🕵️♂️🔍
Let's identify the main nodes and the relevant ties:
- Nodes: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H.
Main ties for applying LKT.
Step 4: Establish the Current Equations 📊
For each node, we apply the LKC. By considering the symmetry of the cube, we can simplify our analysis.
Node A: 𝐼𝐴𝐸 =𝐼𝐴𝐵 + 𝐼𝐴𝐷
Node H: 𝐼𝐻𝐸 + 𝐼𝐻𝐹 + 𝐼𝐻𝐺 = 𝐼𝑡
Step 5: Establish the Stress Equations 📉
For the ties, we apply the LKT. This will allow us to find the voltage drops and relate them to the currents.
Loop A-B-F-H-E: 𝑉=𝐼𝐴𝐵.𝑅 + 𝐼𝐵𝐹.𝑅 + 𝐼𝐹𝐻.𝑅 + 𝐼𝐻𝐸.𝑅
Loop A-D-H-E: 𝑉=𝐼𝐴𝐷.𝑅 + 𝐼𝐷𝐻.𝑅 + 𝐼𝐻𝐸.𝑅
Step 6: Solve the System of Equations 🧮
Now, we solve the system of equations to find the currents in each branch. Because of symmetry, we can consider some currents to be equal. This simplifies the equations.
Currents in Equivalent Resistances:
The total current 𝐼𝑡 is distributed through the resistors symmetrically. We calculate the equivalent resistance 𝑅𝑒𝑞
𝑅𝑒𝑞=5/6.𝑅
With 𝑅=1000Ω
𝑅𝑒𝑞=5/6 . 1000Ω = 833.33Ω
We use Ohm's Law to find the total current 𝐼𝑡:
𝐼𝑡 = 𝑉/𝑅𝑒𝑞 = 𝑉/833.33 Ω
Step 7: Calculate Voltage Drops and Currents in Each Branch ⚙️
For each individual resistor, we calculate the voltage drop using 𝑉 = 𝐼.𝑅 . Considering the total current and uniform distribution, we calculate the currents in each branch.
Calculation Example:
Suppose that the applied voltage 𝑉 is 10V:
𝐼𝑡 = 10𝑉/833.33Ω ≈ 0.012𝐴
Distributing the current between the resistors in parallel:
𝐼𝐴𝐸 = 𝐼𝐴𝐷 = 𝐼𝐴𝐵 = 𝐼𝐻𝐸 = 𝐼𝐻𝐹 = 𝐼𝐻𝐺 ≈ 0.002𝐴
Step 8: Verification of Results ✔️
Finally, we verify the results by summing the voltage drops across the closed loops and ensuring that they comply with the LKT. This gives us certainty that our calculations are correct.
Summary 📝
Solving a mixed circuit of cube-shaped resistors may seem complicated at first, but by systematically applying Ohm's and Kirchhoff's laws, we can decompose the problem and find a precise solution.
I hope this exercise has been as interesting for you as it was for me. Please feel free to comment on your questions or similar experiences solving complex circuits!
Hopefully this detailed explanation will be useful to all the electronics and circuits enthusiasts in the Hive community.
Until the next post! 🚀⚡️